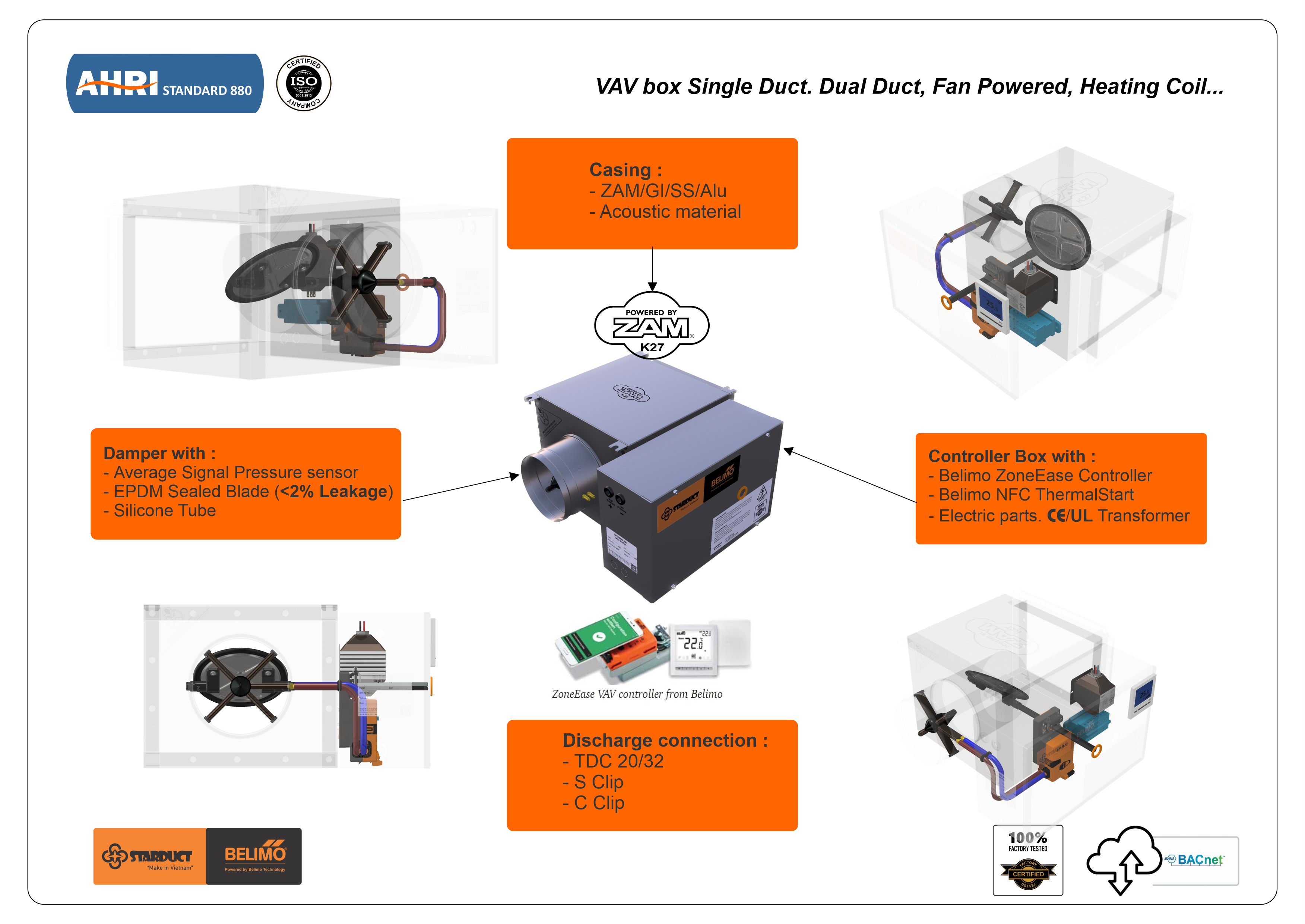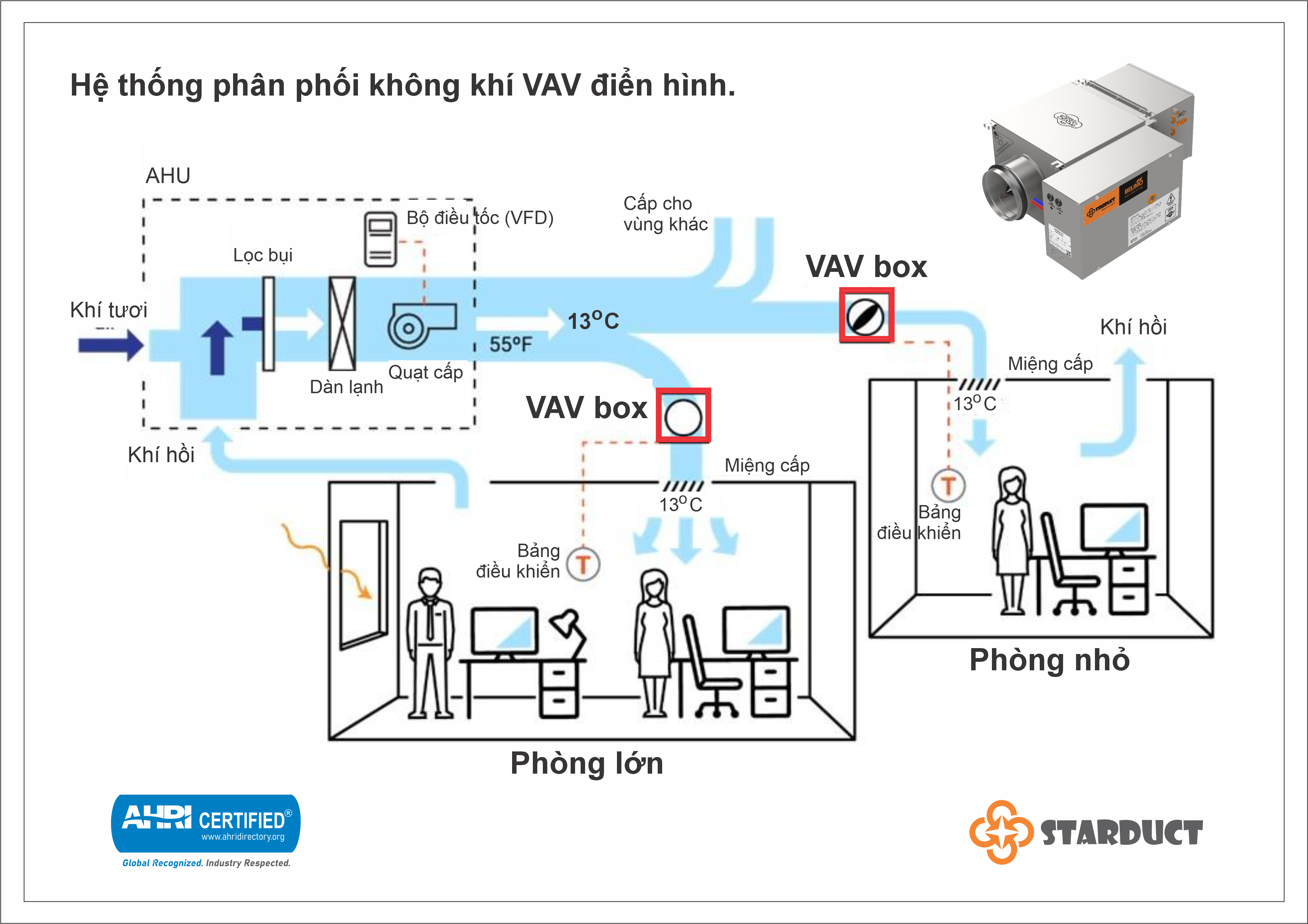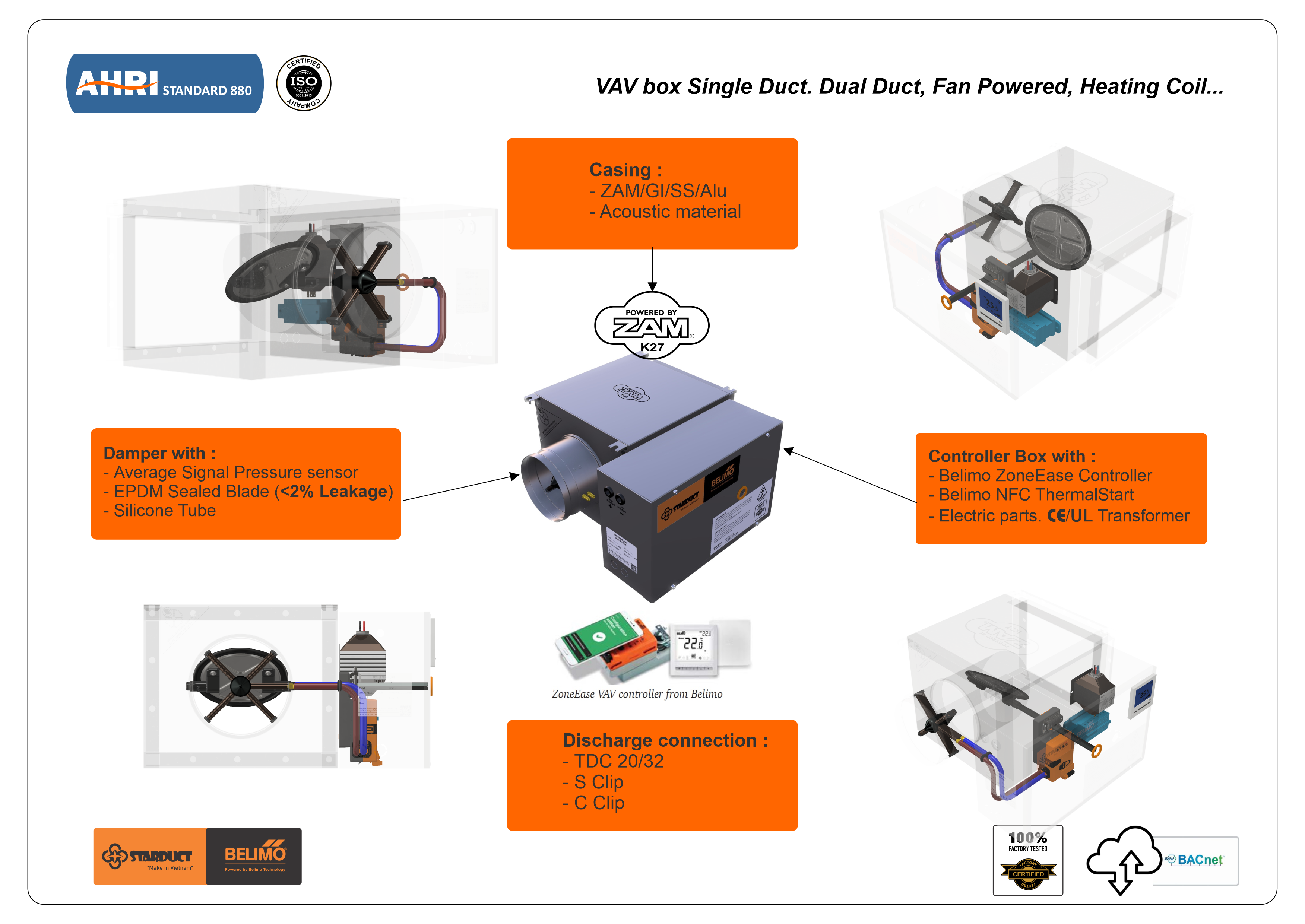
Operating Principle of the VAV Box
In modern buildings, the VAV Box is a vital component of HVAC systems. It silently adjusts the supply air volume based on the actual load of each zone, ensuring comfort, energy efficiency, and quiet operation.
This article explains the VAV Box’s working principle with a clear technical sequence and easy-to-understand calculations.
Initial Setup — The Foundation for Accurate Operation
Each VAV Box is pre-programmed by engineers with:
- ✅ Design airflow (Q_design) – based on the thermal load of the zone.
- ✅ Minimum airflow (Q_min) – ensures minimum fresh air (per ASHRAE 62.1 or project standards).
- ✅ Maximum airflow (Q_max) – capped to reduce noise and save energy.
These values are configured into the VAV Box controller.

Operation Process — Step-by-Step Calculation and Control
Step 1: Receive Actual Load Signal
- A thermostat measures room temperature (or CO₂/humidity sensors for fresh air VAVs).
- Sends temperature/CO₂/humidity signals to the controller.
Step 2: Measure Pressure, Calculate Actual Airflow
The controller receives signals from the VAV Box’s pressure sensor:
- ΔP = P_total − P_static
- P_total = total pressure at the measurement point
- P_static = static pressure at the measurement point
Then calculates air velocity:
- V = K × √ΔP
- V = air velocity at the damper cross-section (m/s)
- K = calibration coefficient provided by the manufacturer (set after balancing)
Then calculates actual airflow:
- Q = V × A
- A = actual open area of the damper (m²), varies with damper angle
Note: For cooling systems, supply air temperature from the AHU is typically ~13°C.
Step 3: Determine Required Airflow
The controller calculates:
- ✅ Thermal load error: ΔT = T_setpoint − T_actual
- ✅ Required airflow: Q_required = f(ΔT, design load, zone parameters)
- ✅ Compares Q_actual and Q_required → decides damper adjustment:
If Q_actual < Q_required → open damper 👉 If Q_actual > Q_required → close damper
If Q_actual is already at Q_min and temperature is still below setpoint → activate heater (if available).
Step 4: Continuous Damper Adjustment
The actuator receives commands and adjusts the damper angle to bring Q_actual closer to Q_required.
Continuous Loop — Sustained Comfort
- ✅ Maintains zone temperature, CO₂, and humidity near setpoints
- ✅ Avoids temperature swings and uncomfortable drafts
- ✅ Saves energy by adjusting precisely to the load
- ✅ Reduces noise by limiting airflow and velocity
.png)
Conclusion
The VAV Box is a smart and precise solution:
- 🌿 Creates optimal microclimates for each zone
- ⚡ Optimizes energy consumption
- 🔇 Delivers quiet, comfortable environments
#VAVBox #HVAC #ComfortEngineering #SmartAirControl #EnergyEfficiency #BuildingTechnology
Bình luận (0)